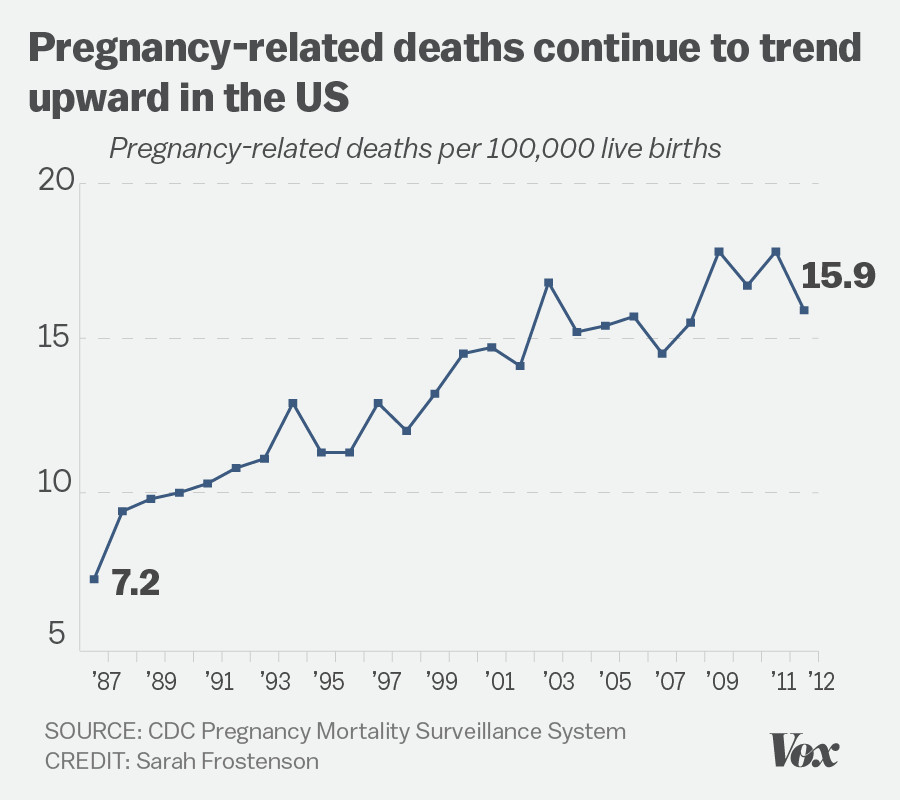
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have alarmingly risen, spotlighting a critical issue in maternal health that demands immediate attention. Despite being one of the wealthiest countries globally, the U.S. leads high-income nations in maternal mortality rates, with more than 80% of these deaths deemed preventable. A recent study reveals that from 2018 to 2022, rates of pregnancy-related deaths increased significantly, highlighting the urgent need for improved prenatal and postpartum care. Furthermore, widespread disparities in maternal mortality among racial and ethnic groups underline the intersection of systemic inequities and health outcomes. It is clear that addressing these alarming trends is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of mothers across the nation.
The rising tide of maternal fatalities in the United States unveils a deeper crisis in maternal well-being, one that transcends mere statistics. As the nation faces a growing number of pregnancy-associated deaths, it becomes evident that comprehensive health solutions are required to combat this troubling trend. Various factors, including inadequate reproductive health services and insufficient support during both prenatal and postnatal stages, contribute to the alarming maternal death rates. Additionally, the persistent racial disparities in birth outcomes portray a daunting challenge that necessitates immediate systemic reform. By understanding and addressing these nuanced issues, we can work towards a future where all women have equitable access to vital maternity care.
Understanding U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
The alarming rise of pregnancy-related deaths in the United States, particularly during the past few years, highlights a critical aspect of maternal health that cannot be ignored. With the U.S. leading among high-income countries in maternal mortality rates, it is crucial to address the multifaceted causes of this phenomenon. Research indicates that over 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, yet systemic issues, including access to quality prenatal care, significantly contribute to the rising mortality rates. These findings emphasize the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to enhance maternal health and minimize the risk of pregnancy-related fatalities.
Furthermore, the disparity in pregnancy-related deaths, particularly among different racial and ethnic groups, reveals an unfortunate truth about healthcare inequities in the U.S. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience nearly four times the mortality rate of their white counterparts. This shocking revelation calls for targeted interventions that address the underlying factors contributing to these disparities. By focusing on equitable access to prenatal care and addressing systemic barriers, we can potentially reduce the incidence of pregnancy-related deaths dramatically.
The Importance of Prenatal and Postpartum Care
Prenatal care is critical for ensuring the healthy development of both the mother and fetus, yet many women face significant barriers that hinder access to such services. Effective prenatal care involves regular health check-ups, monitoring for potential complications, and providing education on healthy pregnancy practices. The ongoing rise in U.S. maternal mortality rates suggests that improvements are urgently needed in how prenatal care is administered and accessed. By expanding healthcare resources and increasing awareness about the importance of attending prenatal appointments, the likelihood of preventing pregnancy-related deaths could significantly improve.
Postpartum care, often overlooked, is equally vital for maternal health. A staggering number of maternal deaths occur after the initial weeks following childbirth, which underscores the necessity of ongoing support during the extended postpartum period. Health systems must shift their approach to view postpartum recovery as a continuum rather than a brief phase immediately following delivery. By adequately addressing both prenatal and postpartum care, healthcare providers can play a pivotal role in reducing maternal mortality rates and enhancing overall maternal health.
Tackling Racial Disparities in Maternal Mortality
Examining the racial disparities in maternal mortality rates reveals systemic issues that cannot be overlooked. Evidence from recent studies shows that non-Hispanic Black women and women from other marginalized groups experience disproportionately high rates of pregnancy-related deaths. Factors contributing to this disparity include socioeconomic inequality, inadequate access to quality healthcare, and the presence of implicit biases within the healthcare system. Addressing these disparities requires a concerted effort to implement policies that ensure equitable access to maternal care for all women, regardless of their race or ethnicity. Educating healthcare professionals about implicit biases and their effects on patient outcomes is essential for fostering an inclusive healthcare environment.
Moreover, community-based interventions that prioritize the needs of underrepresented populations can lead to meaningful improvements in maternal health outcomes. Programs that focus on providing culturally competent care and tackling socioeconomic barriers will help bridge the gap and reduce racial disparities in maternal mortality. Researchers and policymakers must work collaboratively to develop targeted solutions that address the unique challenges faced by racial minorities in accessing quality prenatal care and postpartum support.
Significance of Chronic Conditions in Maternal Mortality
Chronic health conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases and hypertension, play an increasingly critical role in maternal health outcomes. Insights gathered from recent studies indicate a disturbing trend: younger individuals are experiencing chronic conditions that traditionally correlate with older age. This increase raises concerns about the overall health of women entering pregnancy and the implications for maternal health. The link between chronic conditions and pregnancy-related deaths indicates the necessity for improved preconception health programs that prepare potential mothers for pregnancy.
Understanding how chronic conditions can affect pregnancy is also key in providing adequate care before, during, and after childbirth. Tailored approaches to managing chronic conditions among pregnant women could significantly decrease the risk of complications, ultimately saving lives. Healthcare providers need to prioritize comprehensive screenings and management plans that encompass a woman’s health history and present conditions, ensuring that all mothers receive the care they need for a healthy pregnancy and postpartum experience.
Addressing Policy Levers to Improve Maternal Health
Improving maternal health outcomes in the U.S. requires a multifaceted approach that considers various social determinants of health and addresses health policies that impact care delivery. A significant point highlighted in the recent study is the variation in maternal mortality rates across different states, which calls for strategic policymaking. Policymakers must identify effective models, like California’s approach to maternal health, to replicate successful interventions in other regions. By increasing funding to public health initiatives and addressing the gaps in state-level healthcare policies, we can work toward reducing overall maternal mortality rates.
Additionally, it’s crucial to recognize that policies affecting maternal health extend beyond the healthcare system to encompass social and economic factors that influence women’s well-being. Comprehensive maternal health strategies should include access to education, stable housing, and mental health resources. By advocating for inclusive policies that support mothers and families, we can create a healthier environment conducive to reducing pregnancy-related deaths and promoting maternal health equity.
Long-Term Implications of Maternal Mortality Trends
The persistent rise in pregnancy-related deaths poses severe long-term implications for society as a whole. High maternal mortality rates can affect community health, economic stability, and population growth. For communities already facing challenges related to health disparities, the burden of increased maternal deaths can exacerbate existing inequalities. Losing a mother has profound effects on family structures, well-being, and child development, further perpetuating cycles of poverty and health inequality. Understanding these long-term implications is essential for fostering community-wide initiatives focused on maternal health.
Moreover, the increase in maternal mortality rates sends a troubling message about the overall state of healthcare in the U.S. This crisis demands urgent attention and concerted efforts from public health officials, healthcare systems, and policymakers. Investing in maternal health not only advances the well-being of women and families but also safeguards the future of communities by ensuring that every child has the opportunity to thrive in a nurturing and supportive environment.
The Role of Public Health Infrastructure in Maternal Mortality
A robust public health infrastructure is essential for combating the rising trend of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. The recent findings highlighting the increasing rates of maternal mortality indicate that without significant investment in public health, the situation is unlikely to improve. A strong public health system can enhance data collection on maternal health outcomes, track progress over time, and implement impactful interventions. However, budget cuts and deprioritization of maternal health threaten to undermine these efforts, leading to further maternal health crises.
To effectively address maternal mortality, there is a pressing need to elevate maternal health on the public health agenda. Strategies include improving surveillance systems to track maternal deaths accurately, engaging in state-level policy discussions, and investing in innovative health solutions that target the unique needs of pregnant women. A concerted focus on enhancing public health infrastructure can lay the groundwork for monumental changes in maternal health outcomes across the U.S., paving the way towards drastically reducing pregnancy-related deaths.
Future Directions in Maternal Health Advocacy
Advocacy plays a crucial role in shaping maternal health policy and improving outcomes for pregnant women in the U.S. As communities become increasingly aware of the alarming rates of pregnancy-related deaths, advocates are essential for pushing for policy changes that prioritize maternal health. Grassroots movements and organizations focused on maternal care can amplify voices for change and hold policymakers accountable. By creating coalitions that unite healthcare providers, patients, and advocacy groups, it is possible to demand better prenatal and postpartum care that addresses the needs of all mothers.
In addition, engaging with the community to raise awareness about maternal health issues can lead to increased support for initiatives aimed at reducing disparities and promoting equitable healthcare access. Educating the public about pregnancy-related mortality and advocating for systemic changes within the healthcare framework can foster a culture that values maternal health. Ultimately, strong advocacy efforts can drive the national conversation towards comprehensive reforms that reduce maternal mortality and enhance the overall quality of care for pregnant women in the U.S.
Innovative Solutions to Enhance Maternal Care
Innovative solutions are essential for addressing the complexities of maternal health and significantly reducing pregnancy-related deaths. Strategies such as telehealth services can expand access to prenatal and postpartum care for women living in remote or underserved areas. By leveraging technology, healthcare providers can reach more patients, provide timely consultations, and monitor women’s health without the barriers of geographical distance. This approach can facilitate early identification of potential complications, ultimately leading to improved maternal outcomes.
Moreover, integrating mental health support into maternal care programs can address the often overlooked psychological aspects of pregnancy and postpartum recovery. Counseling services, educational programs, and peer support groups can provide women with the resources and emotional support they need throughout their pregnancy journey. By pairing innovative healthcare solutions with comprehensive support systems, we can pave the way for a healthcare model that prioritizes overall maternal health and significantly lowers the rates of preventable pregnancy-related deaths.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
The leading causes of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths include cardiovascular disease, hemorrhage, and hypertensive disorders such as preeclampsia and eclampsia. Concerns have arisen due to the increasing prevalence of chronic conditions among pregnant individuals.
How does maternal health impact pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Maternal health significantly affects pregnancy-related deaths, as chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes, as well as inadequate prenatal care, contribute greatly to maternal mortality rates. Improving maternal health through better care can reduce these deaths.
What role do racial disparities play in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
Racial disparities are a critical factor in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest rates. Systemic inequities in healthcare and social determinants of health contribute to these disparities.
Why do late maternal deaths, occurring after 42 days postpartum, matter in discussions about maternal mortality?
Late maternal deaths are important because they account for nearly a third of total pregnancy-related deaths. Recognizing deaths that occur up to a year postpartum highlights the need for better postpartum care and a comprehensive approach to maternal health.
How can improving prenatal and postpartum care reduce U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
Enhancing both prenatal and postpartum care can significantly lower pregnancy-related deaths by addressing complications early, providing adequate support during and after pregnancy, and ensuring a continuum of care that encompasses the entire reproductive process.
What public health measures are needed to address U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
To address pregnancy-related deaths, public health measures must include investing in maternal health programs, increasing access to quality care, promoting health education, and enacting policies that reduce disparities and improve the quality of care across states.
What changes are necessary to reduce racial disparities in maternal mortality rates?
Reducing racial disparities in maternal mortality rates requires comprehensive policy reform that addresses social determinants of health, expands access to equitable healthcare, and confronts systemic bias in the maternal health care system.
Why is it important to track U.S. pregnancy-related deaths accurately?
Accurate tracking of pregnancy-related deaths is essential for identifying trends, evaluating the effectiveness of health interventions, influencing policy changes, and ultimately driving improvements in maternal health outcomes across the U.S.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
The COVID-19 pandemic initially led to increased pregnancy-related mortality rates, particularly in 2021, highlighting ongoing vulnerabilities in the healthcare system and the need for enhanced maternal care during crises.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Rates | U.S. pregnancy-related deaths increased from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018 to 32.6 in 2022. |
| Preventability | Over 80% of these deaths are considered preventable. |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women have the highest mortality rate at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The sharpest increase in mortality rates occurred in 2021, likely due to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Chronic Conditions | Cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause of pregnancy-related death. |
| Need for Improved Care | Investment in public health infrastructure and innovative solutions is critical for reducing maternal mortality. |
Summary
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are alarmingly high, with the country leading many of its high-income counterparts in maternal mortality rates. Despite being largely preventable, these deaths have continued to rise, highlighting critical gaps in healthcare and the need for systemic improvements. Addressing the significant disparities among racial and ethnic groups, coupled with a focus on holistic maternal care extending beyond the typical postpartum period, is essential for enhancing outcomes. Active investment in public health and innovative strategies is urgently required to turn the tide on this pressing issue.