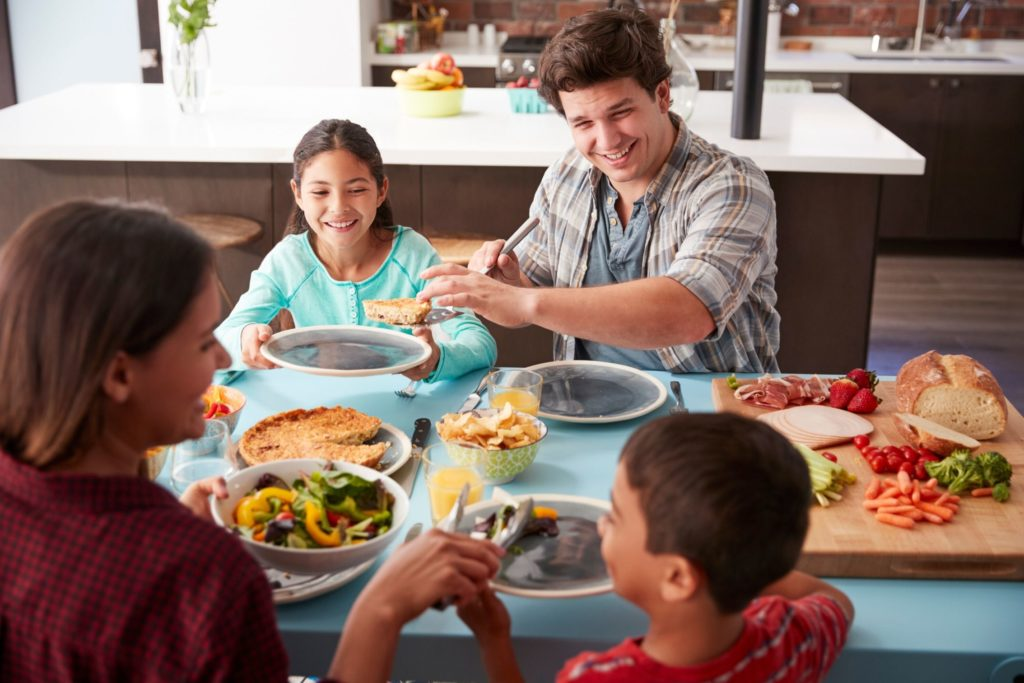
Shared meals and happiness are deeply interconnected, serving as a vital component of well-being in our daily lives. Research consistently shows that individuals who regularly dine with others experience higher levels of life satisfaction and are more likely to exhibit positive emotions. The importance of meal sharing cannot be overstated, as it acts as a catalyst for social connections that foster joy and companionship. In contrast, dining alone is increasingly becoming a norm, with a significant number of Americans reporting solitary eating habits, which could negatively impact their happiness indicators. By valuing shared meals, we can enhance our mental well-being and cultivate stronger relationships, demonstrating that the act of eating together transcends mere sustenance.
The connection between communal dining and joy highlights the significance of social interactions in fostering emotional health. Engaging in meals with friends or loved ones not only nourishes the body but also enriches the spirit, creating bonds that enhance overall happiness. Conversely, solitary dining can lead to feelings of isolation and decreased satisfaction with life. As we examine the effects of meal sharing, we uncover its critical role in building social ties and promoting well-being, asserting that enjoying food in the company of others is essential for a fulfilling life. This exploration into the dynamics of culinary companionship opens up discussions about how lifestyle choices can influence our happiness.
The Importance of Shared Meals in Building Social Connections
Shared meals act as a vital foundation for fostering social connections among individuals. Engaging in communal dining not only offers an opportunity to enjoy delicious food but also encourages meaningful conversations and interactions. These gatherings can create a sense of belonging, enhancing relationships among family members, friends, and even coworkers. When people gather around the table, they establish bonds that can significantly contribute to their overall happiness and emotional well-being.
Furthermore, shared meals can break down barriers between individuals and promote inclusivity. In diverse societies, communal dining can serve as a platform where different cultures and traditions intersect, allowing individuals to connect beyond their differences. By embracing communal meals, people can enhance their social networks, which are crucial for mental health and emotional support.
Dining Alone vs. Shared Meals: Impact on Happiness
The trend of dining alone has been increasingly prevalent, with statistics showing a significant rise in individuals who eat all their meals solo. This shift poses questions about its implications on overall well-being. Studies indicate that those who frequently dine alone may experience feelings of isolation, which can negatively impact mental health. In contrast, individuals who share meals with others consistently report higher levels of life satisfaction and positive emotions, reinforcing the notion that human interaction during meal times is essential for happiness.
While dining alone might sometimes offer convenience, it lacks the emotional richness found in shared meals. The experience of sharing food includes not only the physical nourishment but also the psychological benefits gained from social interaction. Thus, the importance of communal dining cannot be overstated; it stands as a key indicator of happiness and well-being, aligning with the notion that social connections flourish through these shared experiences.
Happiness Indicators: Shared Meals as a Measure
Many researchers are constantly in search of reliable happiness indicators beyond mere financial metrics. Shared meals have emerged as a compelling measure of happiness, providing insights into one’s social life and overall satisfaction. Unlike income, which can vary significantly and is often met with reluctance to disclose, the act of sharing a meal is tangible and easily quantifiable. A simple inquiry about how many meals someone has shared recently can reveal patterns related to social interactions that contribute to their happiness.
The findings indicate that the frequency of meal sharing has a strong correlation with life satisfaction. For instance, individuals who engage in shared meals regularly convey greater emotional fulfillment and connection to others. Therefore, recognizing meal sharing as a true happiness indicator presents an opportunity for individuals and policymakers alike to focus on fostering environments that encourage communal dining and social engagement.
Exploring the Relationship Between Meal Sharing and Well-Being
The investigation into the relationship between meal sharing and well-being is a burgeoning field of interest among social scientists. Researchers like Micah Kaats are eager to determine whether sharing meals directly leads to an increase in happiness or whether naturally happier individuals tend to share more meals. This interplay suggests a complex relationship where both factors may reinforce one another, creating a cycle of increased pleasure and social engagement.
To deepen this understanding, future studies could explore various demographics and their dining habits, decisively linking meal sharing frequency to well-being measures. By scrutinizing these patterns, researchers can begin to comprehend the broader implications of social interactions in fostering happiness and address challenges associated with declining social participation in activities like communal dining.
The Role of Policy in Promoting Shared Meals
As mental health issues and social isolation become growing concerns, the consideration of policies that encourage shared meals could promote a positive shift in community dynamics. Policymakers could initiate programs designed to support communal dining events, encourage local organizations to host meals, or even integrate meal-sharing activities in fellowship programs. Such strategies aim to create community cohesion and provide individuals with opportunities for social interaction that is crucial for maintaining well-being.
Moreover, these policy interventions could be particularly beneficial in urban areas where people tend to feel more isolated despite being surrounded by crowds. By designing inclusive spaces that facilitate shared meals, communities not only uplift their members but also foster healthier social environments where happiness can thrive. This focus on shared meals highlights a potential pathway for initiating action toward improved societal well-being.
The Psychological Benefits of Sharing Meals
Exploring the psychological benefits of sharing meals reveals how dining together contributes to emotional health. Sharing food often fosters an atmosphere of care and connectedness, as individuals interact and bond over their culinary experiences. This interaction can help reduce feelings of loneliness and improve overall mental health, serving as a powerful antidote to the negative impacts of social isolation.
Additionally, the act of meal sharing often involves humor, storytelling, and the creation of memories, all of which play a vital role in enhancing one’s mood and sense of joy. Hence, prioritizing shared meals can be a simple yet effective strategy to bolster mental health, as the joys of communal dining extend far beyond just the food.
Cultural Perspectives on Shared Meals and Connection
Different cultures have unique approaches to shared meals, demonstrating the universal significance of dining together. In many cultures, communal meals are seen as a sacred occasion where family and friends gather, emphasizing the importance of connection through food. These cultural practices not only strengthen social ties but also create an enduring sense of identity and tradition, contributing positively to individual happiness.
Conversely, as global trends shift towards individual dining preferences, understanding these cultural perspectives can provide insights into maintaining strong social connections. By celebrating and incorporating diverse dining traditions, societies can potentially reverse the trend of isolation, reinforcing the idea that happiness can be elevated through shared meals, regardless of cultural background.
Future Directions: Research on Shared Meals and Happiness
The exploration of shared meals as a significant factor in enhancing happiness presents numerous avenues for future research. Establishing causality between communal dining and well-being could provide individuals and communities with actionable insights into improving their lives. Researchers may conduct longitudinal studies to determine the long-term effects of increased meal sharing on happiness indicators across different demographics.
In addition, integrating qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups could enrich our understanding of personal experiences and the subjective value placed on shared meals. By widening the scope of research to include diverse perspectives and contexts, the dialogue surrounding meal sharing and happiness will undoubtedly continue to grow, revealing its profound impact on social well-being.
Encouraging Meal Sharing as a Community Initiative
Communities hold the potential to foster environments that actively promote meal sharing as a viable method to bolster social connections and happiness. Initiatives like community potlucks or shared dining events can encourage individuals to come together, breaking down social barriers and enabling the formation of friendships. Moreover, these initiatives can serve as a platform for addressing issues of food insecurity, creating a culture of support and shared resources.
Moreover, encouraging local businesses to participate in promoting shared meals could cultivate a vibrant community atmosphere. Restaurants might offer discounts for larger groups or host themed nights that emphasize sharing, further integrating the act of dining together into the community’s lifestyle. By prioritizing meal sharing, societies can take a proactive approach towards improving social connections and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do shared meals impact happiness and well-being?
Shared meals significantly enhance happiness and well-being, as studies indicate that people who regularly dine with others report higher life satisfaction and positive emotions. This social connection formed during meals fosters a sense of community and belonging, which are essential indicators of overall well-being.
What is the importance of meal sharing for social connections?
Meal sharing plays a vital role in strengthening social connections. Eating together provides opportunities for interaction, communication, and bonding, all of which contribute to a greater sense of happiness and community. This practice helps combat isolation and enhances interpersonal relationships.
Is dining alone negatively affecting happiness levels?
Yes, dining alone is linked to decreased happiness levels. Research shows that a growing number of Americans are eating meals alone, which correlates with lower life satisfaction and emotional well-being. Sharing meals with others can counteract these effects and promote a positive outlook on life.
What are the happiness indicators related to shared meals?
Happiness indicators related to shared meals include increased life satisfaction, positive emotional expression, and stronger social networks. Studies suggest that the frequency of shared meals is as significant in predicting happiness as income or employment status, highlighting the importance of meal sharing in enhancing overall well-being.
Can sharing meals lead to long-term happiness?
While research indicates a strong correlation between meal sharing and happiness, the specifics of causality are still being studied. However, the practice of sharing meals has the potential to cultivate lasting social connections, which can contribute to sustained happiness and improved mental health over time.
How can policymakers use the concept of shared meals to improve community well-being?
Policymakers can promote community well-being by encouraging initiatives that facilitate shared meals, such as community dinners or cultural food events. By fostering environments where meal sharing is prevalent, they can enhance social connectivity and improve overall happiness and mental health in the community.
What role do cultural factors play in meal sharing and happiness?
Cultural factors significantly influence meal sharing practices and their related impact on happiness. Different cultures prioritize communal eating in various ways, and those traditions often enhance social bonds and promote collective well-being. Understanding these cultural differences can help in recognizing the diverse ways that shared meals contribute to happiness.
How can individuals increase their happiness through shared meals?
Individuals can increase their happiness by actively seeking to share meals with friends, family, and community members. Simple acts like inviting others to join for dinner or participating in group potlucks can enhance social connections, leading to improved happiness and emotional well-being.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Shared meals are more indicative of well-being than income. |
| Dining with others correlates with higher life satisfaction and positive emotions. |
| In 2023, 1 in 4 Americans ate all meals alone, a significant increase from previous years. |
| There is uncertainty whether shared meals directly cause happiness or if happier individuals share meals more often. |
| Tracking shared meals offers a straightforward measure of social connection and potential happiness. |
| Encouraging shared meals may improve well-being and could guide policy interventions. |
Summary
Shared Meals and Happiness are closely linked concepts that highlight the significance of social interactions in our lives. Studies suggest that sharing meals can be a reliable indicator of happiness, potentially more so than financial status. In an era where more individuals are dining alone, it becomes crucial to understand the role of meal sharing in enhancing life satisfaction. Therefore, fostering environments that encourage communal dining could not only strengthen community bonds but also improve overall well-being.